SAP Cloud ALM in Action
.png)
SAP Cloud ALM in Action
Unlocking Real Value: SAP Cloud ALM in Action
In our previous blog post SAP Cloud ALM - The Future of Application Lifecycle Management, we explored the broad capabilities of SAP Cloud ALM and how it empowers organizations to manage their SAP landscapes more efficiently. In this blog, we will deep dive into four powerful use cases that show SAP Cloud ALM in action: Cloud Transport Management Service (CTMS), Unified monitoring of SAP Integration Suite & SAP backend artifacts, Clean Core KPIs, and Document Management.
Use Case 1: Streamlining Deployments using CTMS in SAP Cloud ALM
The Cloud Transport Management Service (CTMS) in SAP Cloud ALM enables seamless transport of software artifacts across SAP Business Technology Platform (BTP) subaccounts.
With development, testing, and production environments spread across different BTP subaccounts, organizations often face following common challenges:
- Manual transport of application artifacts is time-consuming and error prone
- Lack of visibility into transport history and dependencies creates deployment risks
- Coordination between development and operations teams is inefficient
By integrating CTMS with SAP Cloud ALM, organizations can overcome these challenges and transform its software delivery pipeline with following benefits:
1. Automated & Unified Transport Landscape
- Define a clear transport path across subaccounts (like Dev → Test → Prod)
- Manage transports for Integration Suite artifacts, SAP Build apps, UI5 modules, S/4HANA extensions in BTP, etc
- Eliminate silos by bringing all transport activities under one roof
- Automated artifact movement across environments
- Version control and rollback capabilities
- Audit trails for compliance and traceability
2. Cross-Tool Compatibility
- Move iFlows from SAP Integration Suite across environments with full version control
- Transport SAP Build Apps and Work Zone content using the same CTMS pipeline
- Support for multi-target applications (MTAs) and custom extensions built on SAP BTP
3. Centralized Monitoring
- Provides a unified dashboard to monitor transport status, errors, and dependencies
- Real-time visibility into transport progress
- Proactive error handling and resolution
- Seamless collaboration between developers and release managers
4. Secure and Scalable Deployment
- Ensure secure transport using SAP BTP’s identity and access management
Following are some of the business outcomes of using CTMS in SAP Cloud ALM:
- Faster deployment cycles due to automation
- Minimal transport failures thanks to pre-checks and dependency validation
- Improved audit readiness with complete transport logs
- Stronger DevOps alignment through centralized control and transparency
The following solution diagram describes the complete setup for using CTMS in SAP Cloud ALM with multiple subaccounts as below:
- Central Subaccount is the Cloud ALM Subaccount and DEV, TEST and PROD Subaccounts can be any of the following SAP cloud systems:
- SAP Build: SAP Build Apps, SAP Build Workzone and SAP Process Automation.
- SAP Integration Suite: Cloud Integration, API management and Open Connectors.
- SAP Extension Suite: CAP (Cloud Application Programming) projects, CAP services and UI5 apps.
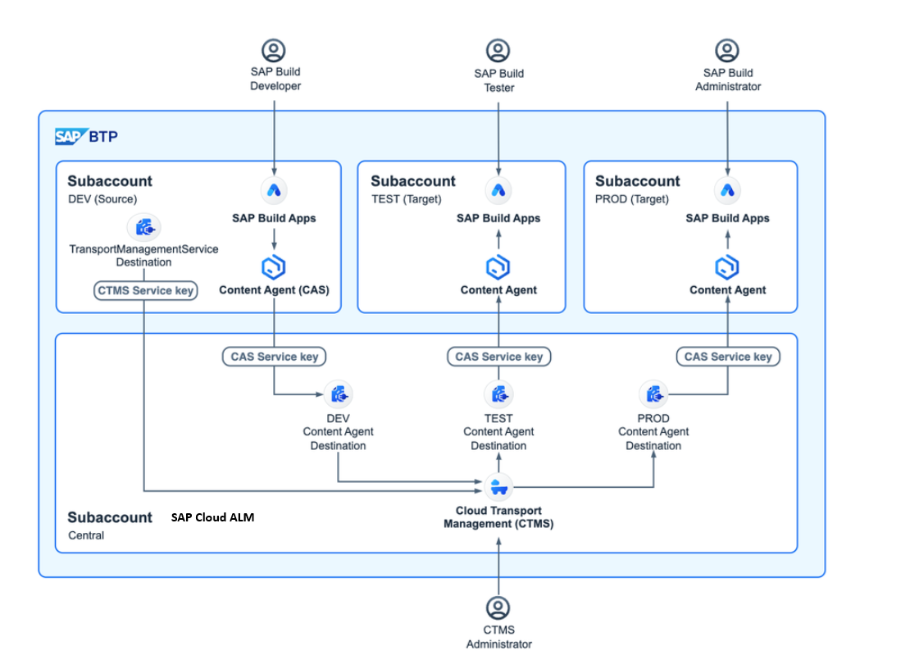
Source: SAP
Use Case 2: Unified Monitoring of SAP Integration Suite and SAP Backend Artifacts
SAP Cloud ALM provides centralized monitoring for SAP Integration Suite, offering a more intuitive UI than the standard Message Processing Log of Integration Suite.
SAP Cloud ALM’s Integration & Exception Monitoring provides deep insights into message flows and integration artifacts across SAP BTP and connected systems. Following artifacts can be monitored as part of SAP Integration Suite Monitoring:
- iFlows and APIs: Track message processing status, latency, and failures.
- Exceptions and Errors: Identify technical and business errors in real time.
- Interface Health: Monitor throughput, retry behavior, and payload issues.
- Alerting & Notifications: Configure alerts for failed messages or performance thresholds.
SAP Cloud ALM extends its monitoring capabilities to backend systems like SAP S/4HANA and SAP ECC 6.0 EHP 8 or higher through SAP Cloud Connector, ensuring operational stability and performance. Following artifacts can be monitored:
- Background Jobs: Track scheduled jobs, execution status, delays, and failures.
- ABAP Short Dumps: Monitor frequency, error types, and affected programs.
- System Performance: Analyze CPU usage, memory consumption, and response times.
- Security & Configuration: Detect misconfigurations, unauthorized changes, and compliance risks.
- Business Process Monitoring: Allows for monitoring processes like Lead to Cash, Source to Pay, Recruit to Retire and Design to Operate. Business Process Monitoring is supported only for S/4HANA system but not for ECC system.
- Real User Monitoring: tracks every request executed by end users to analyze past performance issues.
These features require the ECC system (ECC 6.0 EHP 8 or higher) to be registered in SAP Cloud ALM via the Landscape Management Service and connected through SAP Cloud Connector.
Unified Monitoring with SAP Cloud ALM bridges the gap between cloud and on-premise operations:
- Centralized view with end-to-end visibility: View integration and backend health in one dashboard.
- Proactive Alerting: Catch issues before they escalate.
- Performance Optimization: Identify bottlenecks and improve system efficiency.
- Governance & Compliance: Maintain audit trails and enforce operational standards.
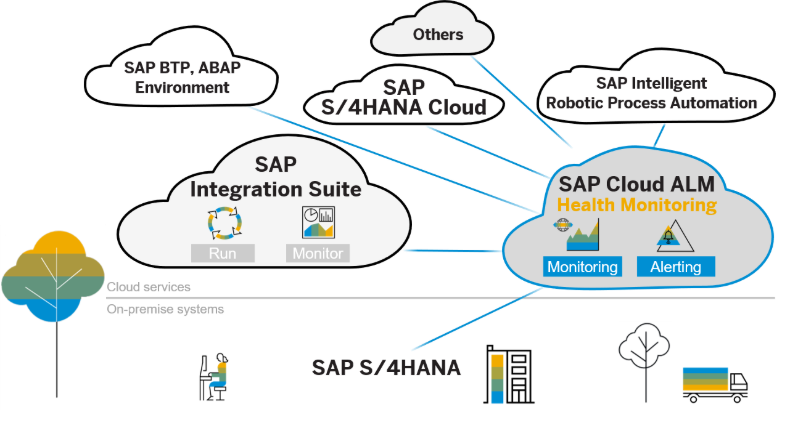
Source: SAP
Use Case 3: Tracking Clean Core KPIs with SAP Cloud ALM
The SAP clean core strategy is a set of principles designed to minimize technical debt and complexity by keeping the core of an SAP system as close to the standard as possible. Maintaining a “Clean Core” is essential for agility, stability and upgrade readiness of SAP systems. SAP Cloud ALM supports the SAP Clean Core strategy by offering dashboards that track adherence to following Clean Core principles:
- Extensibility Analysis: Track usage of custom code, in-app extensions, and side-by-side developments.
- Integration Health: Monitor interface usage, message volumes, and error rates.
- Operational Metrics: Evaluate job performance, system load, and exception handling.
- Process Compliance: Assess adherence to SAP Best Practices and standard workflows.
- Data Quality: Identify inconsistencies, duplicates, and outdated records.
Extensibility KPIs in Cloud ALM
Within the System View dashboard of SAP Cloud ALM, following extensibility-related KPIs can be monitored to evaluate custom code health and compliance with clean core principles:
- Custom code inventory: Provides an overview of all custom code in the system, helping to track the total volume and evolution of custom extensions.
- Compliance with cloud standards: Measures whether custom code adheres to SAP's extensibility framework, such as using only released APIs and technologies.
- Usage patterns and performance impact: Tracks the actual usage of custom objects to identify unused or obsolete code. It also assesses the performance impact of custom code to prevent potential system slowdowns.
- Impact of system updates: Evaluates how custom code might be affected by future SAP system upgrades, allowing for proactive remediation planning.
Following are some of the clean core KPI Examples:
- % of custom objects vs standard objects
- Number of active iFlows and their error rates
- Frequency of short dumps and failed jobs
- Ratio of standard vs modified business processes
By continuously monitoring these metrics, organization can achieve to:
- Reduce custom code footprint
- Improve integration reliability
- Achieve full compliance with SAP’s clean core guidelines
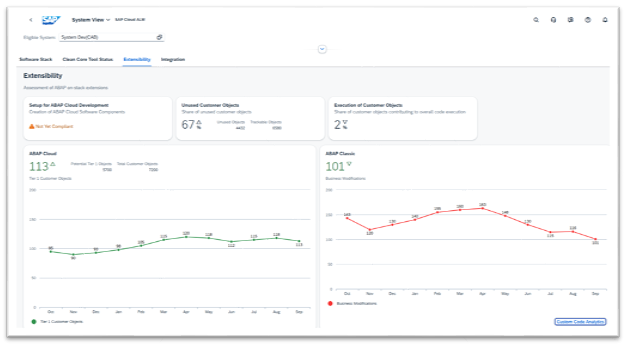
Source: SAP
Use Case 4: Document Management Made Easy with SAP Cloud ALM
Traditionally, project documents are stored across multiple platforms like shared drives, emails, local folders, or third-party tools. This leads to:
- Difficulty locating the latest version of a document
- Lack of traceability between documents and project tasks
- Compliance risks due to missing or outdated documentation
SAP Cloud ALM document management overcomes these challenges and simplifies document handling by allowing users to upload, categorize, and link documents directly to project workflows, tasks and processes with following benefits:
- Central Repository: Upload and store documents in one place, accessible to all project stakeholders.
- Contextual Linking: Attach documents directly to tasks, requirements, test cases, or user stories - so everything is where it belongs.
- Version Control: Maintain document history and ensure teams are always working with the latest version.
- Access Control: Define who can view, edit, or upload documents, ensuring security and governance.
- Audit Readiness: Keep a clear trail of documentation for compliance, validation, and post-project reviews.
These four use cases demonstrate how SAP Cloud ALM delivers tangible value - by accelerating deployments, enhancing visibility across integrations and backend systems, supporting Clean Core initiatives, and simplifying project documentation.
Based on our customer implementations, Neomore brings deep expertise in integrating SAP Cloud ALM into diverse SAP landscapes. We ensure alignment with your governance models, operational processes, and strategic priorities.
Read our previous blog about ALM: SAP Cloud ALM - The Future of Application Lifecycle Management
Ready to explore what SAP Cloud ALM can do for your organization?
Book a demo or get in touch with our experts to start your journey toward smarter SAP operations.
Contact Us


.png?width=1024&height=1024&name=Frame%2016%20(1).png)